Some of the leading insurance providers in India derive the better part of their premiums from banking channels. Bancassurance has been the most prominent distribution channel for life insurers since 2017. These include SBI Life (public sector) and HDFC Life (private sector), which derive 60% of their revenues from their parent banks, i.e., State Bank of India and HDFC Bank, respectively. Lately, Indian regulatory bodies have paid cognisance to the prevailing malpractices affecting customer trust. This has prompted regulatory reconsideration and tighter oversight.

What is Bancassurance?
Bancassurance is a strategic partnership in which the insurance provider uses a bank’s distribution channels to sell its products and services to customers. The arrangement enables the bank to multiply its revenue streams and the insurer to expand its customer base.
"The World Bank considers bancassurance “a valuable tool for developing insurance in emerging markets.”
Source: World Bank
A Brief History of Bancassurance Evolution
The foundations of bancassurance go back to the 1970s in France. This is when life insurance was sold to high-net-worth individuals through banking channels. Spain too was an early adopter of bancassurance services in banking by the 1980s.
Much like any new idea, bancassurance faced its share of criticism. It was initially considered a potential risk to the security of financial systems. This is because it was assumed that bancassurance could give banks excessive control over financial products.
Later, with regulations in place, bancassurance emerged even stronger in Europe and entered Asia in the 1990s. Since then, the evolution of bancassurance has only looked upwards.
Countries with massive population growth, such as India and China, were the first adopters. The importance of bancassurance for these nations lies in its ability to seamlessly enhance banking offerings with insurance products. Through an amendment to the Banking Regulation Act of 1949, the government of India permitted banks to distribute insurance products under Section 6(1)(o).
Banks became a popular distribution channel for insurance products, which had lesser perceived importance and trust. The 1990s also marked the beginning of selling non-life insurance products via bancassurance channels. India Stats
India Stats
₹64,613 Crores – Total life insurance premiums from bancassurance channels in FY2023.
14.1% – Share of policies covered by bancassurance in FY 2023
How Bancassurance Works
In essence, bancassurance is the distribution of insurance via banking channels, meaning banks do not develop or directly sell insurance products. To gauge the true meaning of bancassurance, it is crucial to understand the role of each stakeholder:
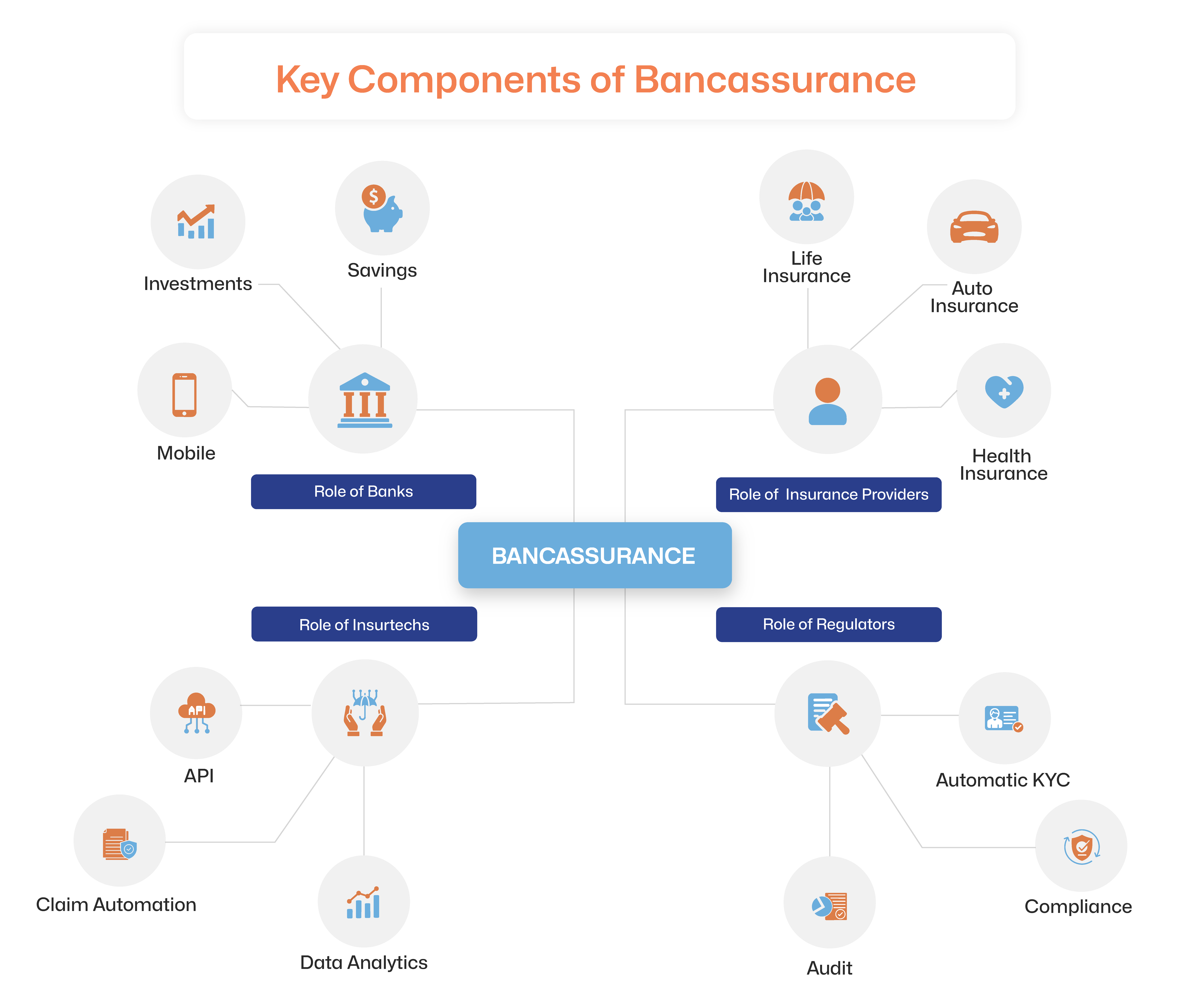 Bancassurance leverages key principles of open finance and open insurance. Open finance paves the way for consented data sharing among financial institutions. Open insurance enables the use of insights from this data for the development of personalised products and distribution via the most suitable banking channels.
Bancassurance leverages key principles of open finance and open insurance. Open finance paves the way for consented data sharing among financial institutions. Open insurance enables the use of insights from this data for the development of personalised products and distribution via the most suitable banking channels.
This relationship fosters an ecosystem for the two industries to collaborate and offer integrated products and services. This maximises benefits for customers while improving operational efficiency for both parties.
Role of Digitalisation
Digital transformation plays a prominent role in reshaping bancassurance, with mobile and internet banking becoming primary channels for insurance sales. This shift caters to the modern customer’s preference for convenience and accessibility. AI-driven chatbots and digital advisors enhance engagement by providing real-time support and personalised recommendations.
Cutting-edge technologies streamline customer journeys, offering instant policy information and claims assistance. Embedded insurance plays a pivotal role by integrating insurance directly into digital banking journeys. For instance, travel insurance can be offered during flight bookings within a banking app. This contextual integration simplifies the purchase process, providing seamless, on-demand coverage. Digital platforms and embedded solutions enhance customer satisfaction, expand market reach, and optimise the operational efficiency of bancassurance processes.
Bancassurance Business Models
Here’s a look at the most popular bancassurance business models.
Distribution Agreements
This is the simplest model, where the bank sells insurance on behalf of insurers. The agreement or regulations may restrict the bank from distributing the products of only one partner. This is a payout-based arrangement, where the bank earns a commission on every sale or premium, depending on the terms of the agreement.
Strategic Alliances
The bank plays a greater role in product development and distribution management. Often, the bank and insurer co-develop insurance products tailored to the needs of banking customers. This allows the bank to employ targeted distribution techniques. However, all liabilities and risks are borne by the Digital insurance company.
For example, City Union Bank has 8 bancassurance partnerships with life (3), general (2) and health (3) insurance carriers. This empowers the bank to offer all-around protection.
Joint Ventures
This kind of model works for banks and insurers of similar size. The bank and insurer join forces to create exclusive offerings, apply targeted marketing strategies and can even share profits. The goal of the joint venture is to create a profitable bancassurance line of products and services to make the most of opportunities emerging through the model. Technologies, such as insurtech and regtech, play a critical role in empowering collaborative market analysis, product development and distribution.
Citibank, for instance, has partnered with the US-based Travelers Insurance. This allows the bank to leverage customer data to identify the opportunity or discover people who are already buying travel insurance from diverse sources. The bank can ease their lives through its collaboration with the insurer by offering personalised embedded insurance products.
Full Integration
This type of collaboration involves a bank developing an insurance subsidiary or acquiring an insurance company to expand its business. The acquisition can happen the other way around as well. In both scenarios, the clause “banking channels distribute insurance products” remains as is.
The most prominent examples of fully integrated bancassurance are SBI and HDFC, which have dedicated life insurance subsidiaries, SBI Life and HDFC Life, respectively.
Benefits of Bancassurance
Bancassurance partnerships are mutually beneficial for both enterprises and their customers.
For Banks
Increased Revenue Streams
Bancassurance creates several opportunities to multiply the bank’s revenue streams. The bank sells insurance products through a commission-based model. The partner bank can also leverage customer data to cross-sell other banking products or share data with the insurer. This lowers the bank’s dependence on revenue from conventional products.
Enhanced Customer Loyalty and Engagement
Banks traditionally enjoy customers’ trust. Adding protection to their offerings through bancassurance strengthens customer relationships, boosting engagement and loyalty.
Differentiation from Competitors
Bancassurance partnerships enable banking institutions to position themselves ahead of their competitors. This is especially helpful in rural areas where insurance access is low. This also improves banks’ value proposition, enabling them to become full-service financial services centres.
For Insurance Companies
Expanded Distribution Network
Bancassurance is a critical tool in bridging the massive gap between insurance and banking penetration. Banks have extensive distribution networks and long-standing customer relationships. Insurers can leverage existing customer bases to offer targeted products and services. In addition, insurers can bundle their products with their partner bank’s offerings while acquiring new clients simultaneously.
In 2021, global banking penetration stood at 76% while till 2022, insurance had reached only 6.7% of the global population.
Source: World Bank
Lower Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Bancassurance allows insurers to operate without the need for branches or agents. This significantly lowers distribution costs. Insurance providers use banking data to pitch targeted products to their customers, which lowers marketing expenditure. 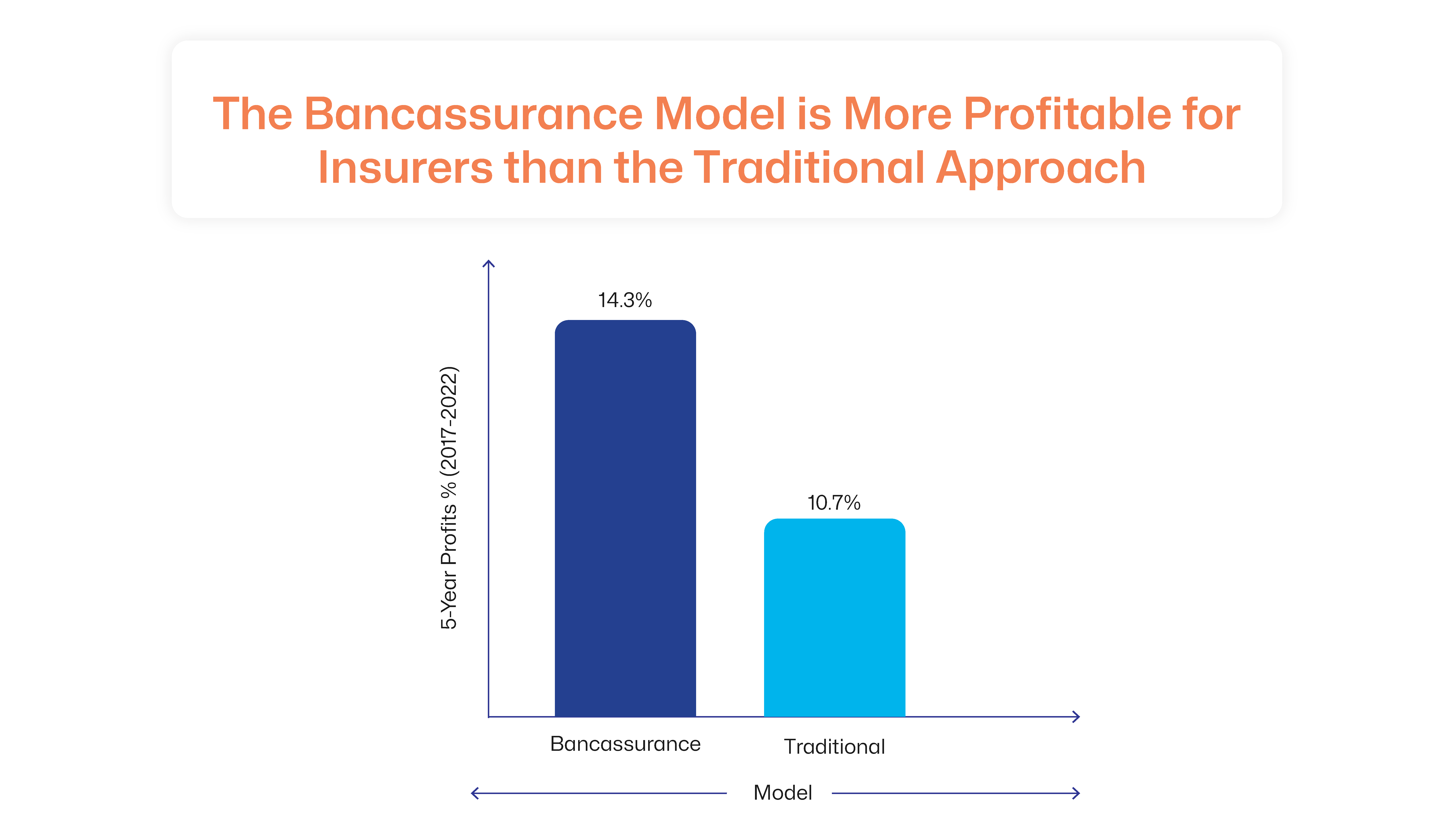 Source: BCG
Source: BCG
Access to a Wider Audience
Insurance providers can access a large pool of customers and their data. They get opportunities to enhance brand visibility and establish credibility through targeted offerings. This also improves their risk assessment, which translates into the ability to expand their offerings for the widening audience. Insurers can expand to new markets via banking channels trusted by customers in those regions.
For Policyholders
Convenience of Purchasing Insurance at Their Trusted Bank
The most significant benefit of bancassurance for a customer is increased accessibility of insurance products. They can purchase life, health, or other types of coverage from trusted financial partners.
Simplified Documentation and Payment Integration
Banks already have detailed customer data through KYC, which reduces the lengthy documentation processes necessary for insurance. Insurtech enables data sharing and automated beneficiary additions to further ease the process. Banks also have recurrent, partial and other forms of payment mechanisms in place. These assist policyholders in paying premiums conveniently and consistently, staying covered.
Better Customer Service and Support
Bancassurance allows customers to have a single point of contact for their banking and insurance needs, simplifying financial planning. Banks have established 24/5 digital customer service channels, which work for all kinds of insurance-related concerns as well. With all customer data in one place, both the bank and insurer can provide cohesive personalised services, elevating the customer experience.
Greater Personalisation
Bancassurance offers a 360-degree view of customers’ financial situations to both the banking and insurance partners. Powered by insurtech, both institutions can predict and create offerings that meet customers’ needs. Greater personalisation ensures more coverage and customer trust.
Bancassurance Challenges & Ways Technology Addresses Them
The top challenges for bancassurance growth are:
Regulatory Compliance & Licensing Issues
Bancassurance is subject to stringent regulatory oversight in most jurisdictions to ensure efficient financial crime detection and prevention. While the specific regulatory frameworks vary across countries, the overarching goals remain consistent: consumer protection, fair competition and maintaining the stability of the financial ecosystem.
Regulatory aspects of bancassurance typically include:
Licensing and Registration
Banks and insurance companies must obtain licenses and register with the respective authorities as bancassurance providers.
Disclosure Requirements
Transparent disclosure of the bank-insurer relationship, including commissions and fees, is required. This is crucial for anti-money laundering (AML) compliance, which requires robust Know Your Customer (KYC) and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) processes.
Product Approval
In certain jurisdictions, insurance products offered through bancassurance channels require regulatory approval from a designated authority.
Data Protection
All sharing of data between the bank and insurer must adhere to stringent regulations. Also, both institutions must acquire consent for using customer data for any purpose.
Capital Requirements
Both financial institutions must meet specific capital adequacy standards when engaging in bancassurance. Some jurisdictions may allow capital management on a shared-risk basis.
B. Lack of Insurance Awareness among Bank Customers
One of the reasons customers fall prey to mis-selling is their lack of awareness.
Difficulty Understanding Complex Products
Customers often have only a limited understanding of insurance products, their features and benefits. This knowledge gap makes them vulnerable to mis-selling. Insurance jargon can be complex and hinder comprehension.
Passive Acceptance
Customers often leave it to their banking advisor to recommend suitable products, without detailing their insurance needs. This trust leads to accepting policies without carefully assessing the benefits. This may also make customers vulnerable to unscrupulous sales personnel who use this trust for ulterior motives.
Bundling
Sometimes, insurance products are bundled with other banking products. This can lead to the customer purchasing insurance they do not need or want.
C. Customer Trust and Conflict of Interest
For regions like Vietnam and the Philippines, where customers lack trust in most financial products, insurance via banking channels faces significant trust issues.
Erosion of Trust
A perception of bank representatives prioritising insurance sales over customers’ best interests in bancassurance can erode trust in the banking relationship. This, along with instances of mis-selling or aggressive sales tactics, can hurt customer confidence in the bank.
Conflict of Interest
Bank employees who are incentivised for insurance sales may compromise objectivity, leading to a conflict of interest. They may end up recommending products that feed their own interests more than those of the customer.
Transparency and Disclosure
Banks may not transparently state their role as only a distributor and conceal commissions and fees charged to acquire bancassurance customers. This lack of transparency may result in loss of trust.
Addressing these challenges requires a strong commitment to ethical sales practices, robust compliance frameworks and a focus on customer education and empowerment.
D. Operational and Technology Challenges
Banks and insurance providers follow different operational approaches and are transitioning to digital operations at various paces. This results in specific challenges that need to be addressed in each partnership.
Manual Processes
The agent-based technique of manually selling insurance increases the workload on banking professionals. This may lead to overworking or a conflict of interest among appointed distribution personnel.
Incomplete Understanding
Banking professionals often lack a complete understanding of insurance products and policy terms, which leaves potential customers with a subpar experience, deterring them from converting.
Limited Expansion
Reliance on physical offices and manual agents is cost-intensive and non-scalable. This translates into distribution constraints, which weigh on bancassurance growth.
How Insurtech Addresses Bancassurance Challenges
Bancassurance leverages cutting-edge technologies for automation, data analysis, enforcing policy terms and streamlining claims management.
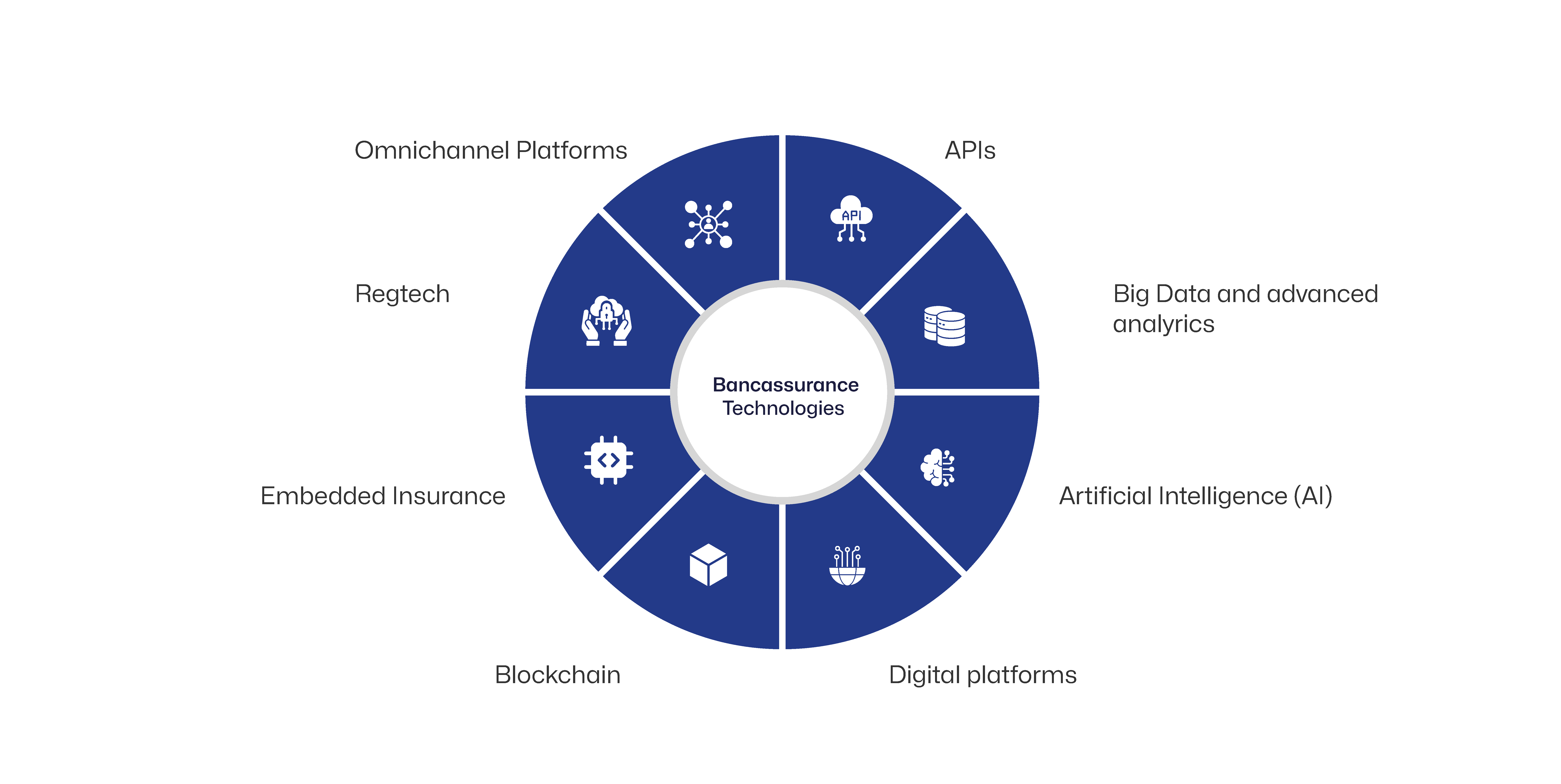
APIs: Secure and Real-Time Data Sharing
APIs enable seamless integration of banking and insurance, allowing real-time data transfer and enhancing customer experience.
Big Data and Advanced Analytics: Data-Driven Insights
Insurtech empowers bancassurance partners to leverage large-scale data processing to uncover actionable insights into customer behaviour, risk assessment and market trends. It also enables predictive analytics and machine learning to personalise services and optimise operational efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enhanced Decision-Making
AI enables automation of several processes, including underwriting, claims processing and fraud detection, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy. AI-powered chatbots can offer instant customer support and personalised recommendations.
Digital Platforms: Effortless Customer Experiences
Intuitive and user-friendly online and mobile platforms simplify access to insurance products and services. Customer-centric platforms are equipped with self-service capabilities to empower customers and increase engagement.
Blockchain: Transparency and Security
Distributed ledger technology helps insurers create immutable records, enhancing trust and transparency in data exchange and transaction processing.
Embedded Insurance: Integration with Banking Platforms
Embedding insurance within banking journeys facilitates contextual recommendations in real-time. Bundled products streamline the sales process and increase insurance penetration. No wonder, 94% of insurers consider embedded insurance critical to their future strategy.
Regtech: Automating Compliance and Fraud Prevention
Automated KYC/AML processes streamline identity verification and risk assessment, while real-time reporting ensures efficient regulatory compliance. AI-powered fraud detection identifies suspicious activity, while automated compliance workflows manage policy updates. Plus, enhanced data security protects sensitive information.
Platforms: Delivering Cohesive Experiences
Omnichannel bancassurance presence enables consistent experiences across channels and platforms, including apps, chatbots and online banking, ensuring seamless customer journeys. AI chatbots offer instant support, and mobile access allows convenient policy management. Personalised portals provide self-service, while integrated communication delivers timely updates.
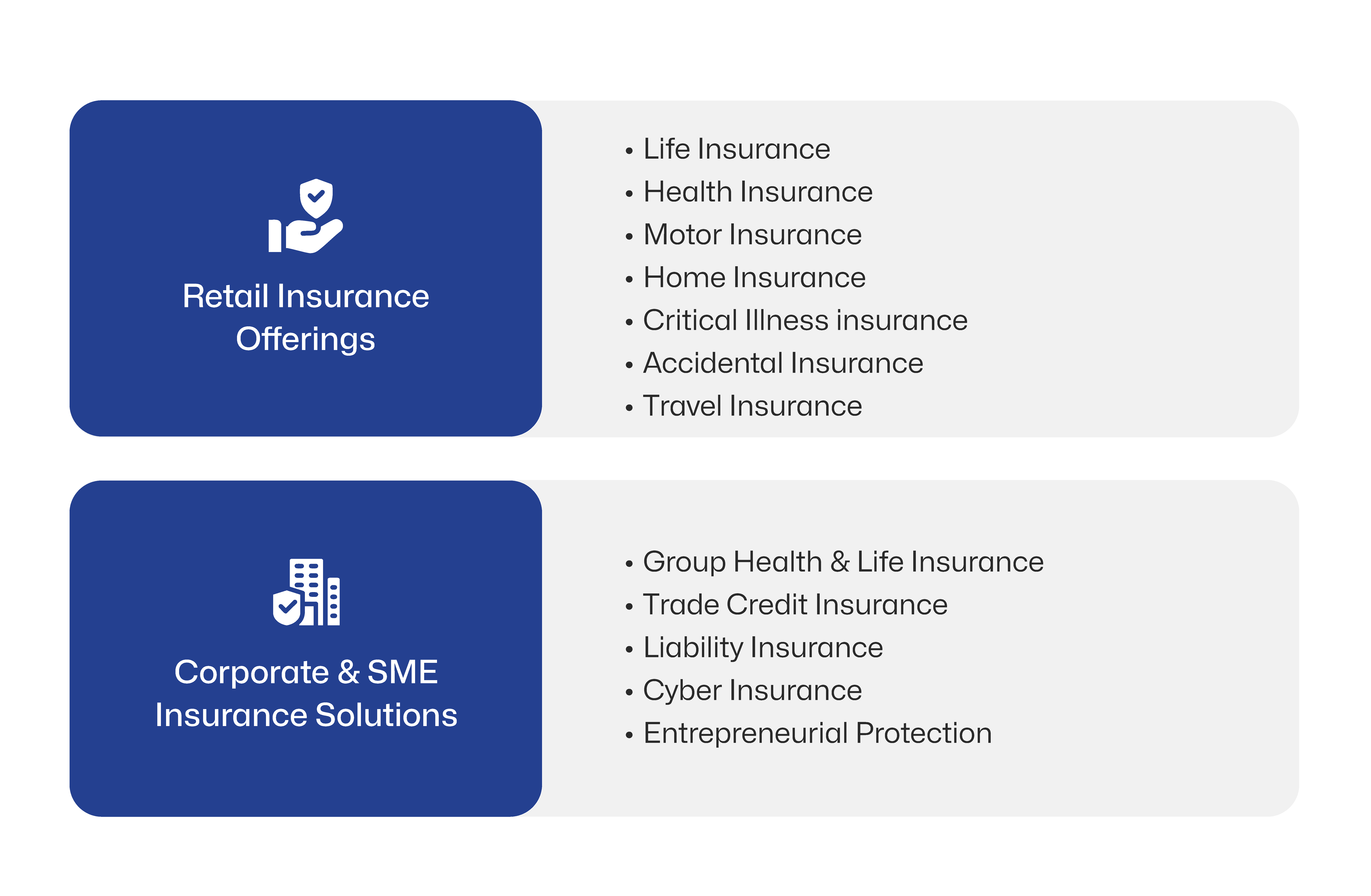
Types of Insurance Products Sold via Bancassurance
Bancassurance products can be categorised based on the needs they fulfil. Bancassurance product types fall into one of the following categories:
Savings Products
This category includes unit-linked plans (ULIPs) or participating endowments, where the policyholder benefits from the accumulated cash surrender value. The protection component is minimal.
Credit Protection Products
Loans or credit cards are often bundled with insurance products specifically designed to pay the customer’s liability, such as a home loan, in the event of their death.
Non-Retail Products
These are designed for businesses of varied sizes to ease capital management and provide support during financial crises.
Standalone Protection
These are targeted insurance products to help clients improve their financial planning. They include needs-based financial plans, such as sachet insurance, critical illness cover, etc.
Innovative Bancassurance Products
Technological advances have made it easier and faster to create and distribute new products. Insurtech empowers banks and insurers to offer innovative protection covers, clubbed with banking products, to amplify reach and penetration.
Pay-As-You-Use Insurance
These are floating plans that blend savings and event-triggered coverage. Customers build a savings buffer within their bank account, which also acts as an insurance pool. Coverage activates only when specified events occur, providing flexible protection and financial security.
Loan-Linked Insurance
Mortgage protection and credit life insurance alleviate debt burdens. In the event of a borrower’s death, these policies settle outstanding loan balances. This safeguards dependents and ensures financial stability, preventing property loss or debt inheritance.
Microinsurance for the Unbanked Segments
Tailored for the underserved populations, microinsurance offers affordable coverage for specific risks. Leveraging banking networks, it extends financial protection to those traditionally excluded from the system, promoting financial inclusion and fostering resilience against unexpected events.
Investment-Linked Insurance
These products merge investment growth with insurance protection. They lower entry barriers to financial management by enabling customers to simultaneously invest and insure. This dual purpose fosters financial growth and encourages long-term planning while providing essential coverage.
Retirement Protection and Pension Products
Annuities and retirement-focused insurance secure financial stability for the elderly. They provide consistent income streams, ensuring a comfortable retirement. These products help individuals manage longevity risks and maintain their desired lifestyle.
Sachet Insurance
Offering targeted, short-duration coverage, sachet insurance addresses targeted needs with affordable premiums. These bite-sized policies protect against niche risks, making insurance accessible for smaller, immediate needs and simplifying the purchase process.
Regulatory Framework for Bancassurance in India
Bancassurance is a significant insurance distribution channel in India. It operates within the guardrails of the oversight of the RBI and IRDAI.
A. Key Regulations Governing Bancassurance in India
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) Guidelines
The IRDAI plays a crucial role in regulating bancassurance activities. Its guidelines cover several aspects, such as:
Suitability of insurance products for bank customers
Disclosure requirements and transparency in sales practices
Handling of customer complaints and grievances
Prevention of mis-selling and coercive practices
Since September 2024, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has been considering capping the contribution of a parent bank to an insurer's total bancassurance business at 50%. The aim is to reduce over-dependence on a single distribution channel and to mitigate systemic risks. However, a concrete regulatory framework is yet to be finalised.
Banking Regulation Act, 1949
The Act governs the operations of banks in India and includes provisions related to their involvement in non-banking activities, including insurance distribution. It ensures that bancassurance activities do not compromise the core banking functions.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Guidelines
The RBI issues guidelines related to banks’ involvement in bancassurance, focusing on risk management, capital adequacy and prevention of conflicts of interest. The RBI and IRDAI work together to ensure that the banking and insurance sectors work in harmony.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Norms
Bancassurance organisations must adhere to PMLA and KYC regulations to ensure customer due diligence and safeguard against financial crime.
B. Licensing Requirements for Banks to Sell Insurance
The IRDAI Corporate Agency License is mandatory for bancassurance partners in India. It applies to banks intending to distribute insurance products. The license specifies the types of insurance products that the bank is authorised to sell (life, non-life, or both). Requirements for the license include:
Eligibility Criteria
These include financial soundness, infrastructure and trained personnel, in addition to demonstrating the ability to comply with the IRDAI guidelines and consumer protection norms of the financial industry.
Training and Certification
Bank employees involved in insurance sales must undergo mandatory training and certification to ensure they have adequate knowledge of insurance products and regulations. This ensures that the customer is being sold a product that fits their needs.
C. Digital Compliance Tools (Regtech) are Simplifying Regulatory Processes
Automated KYC and AML Checks
Regtech solutions automate KYC and AML checks, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy. This speeds up customer onboarding and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting
Digital compliance tools enable real-time monitoring of transactions and activities, facilitating early detection of potential risks and compliance breaches. Automated reporting features streamline the submission of regulatory reports.
Compliance Automation
Regtech helps automate compliance workflows, such as policy updates, risk assessments and audit trails. This reduces the burden of manual compliance tasks and minimises the risk of errors.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI-powered regtech solutions can analyse large volumes of data to detect patterns of fraudulent activity. This allows red flags to be raised early, helping prevent financial losses and maintain regulatory compliance.
Digital Audit Trails
Regtech solutions create digital audit trails, providing a transparent and auditable record of all compliance-related activities. This makes it easier for regulators to conduct audits and ensure accountability.
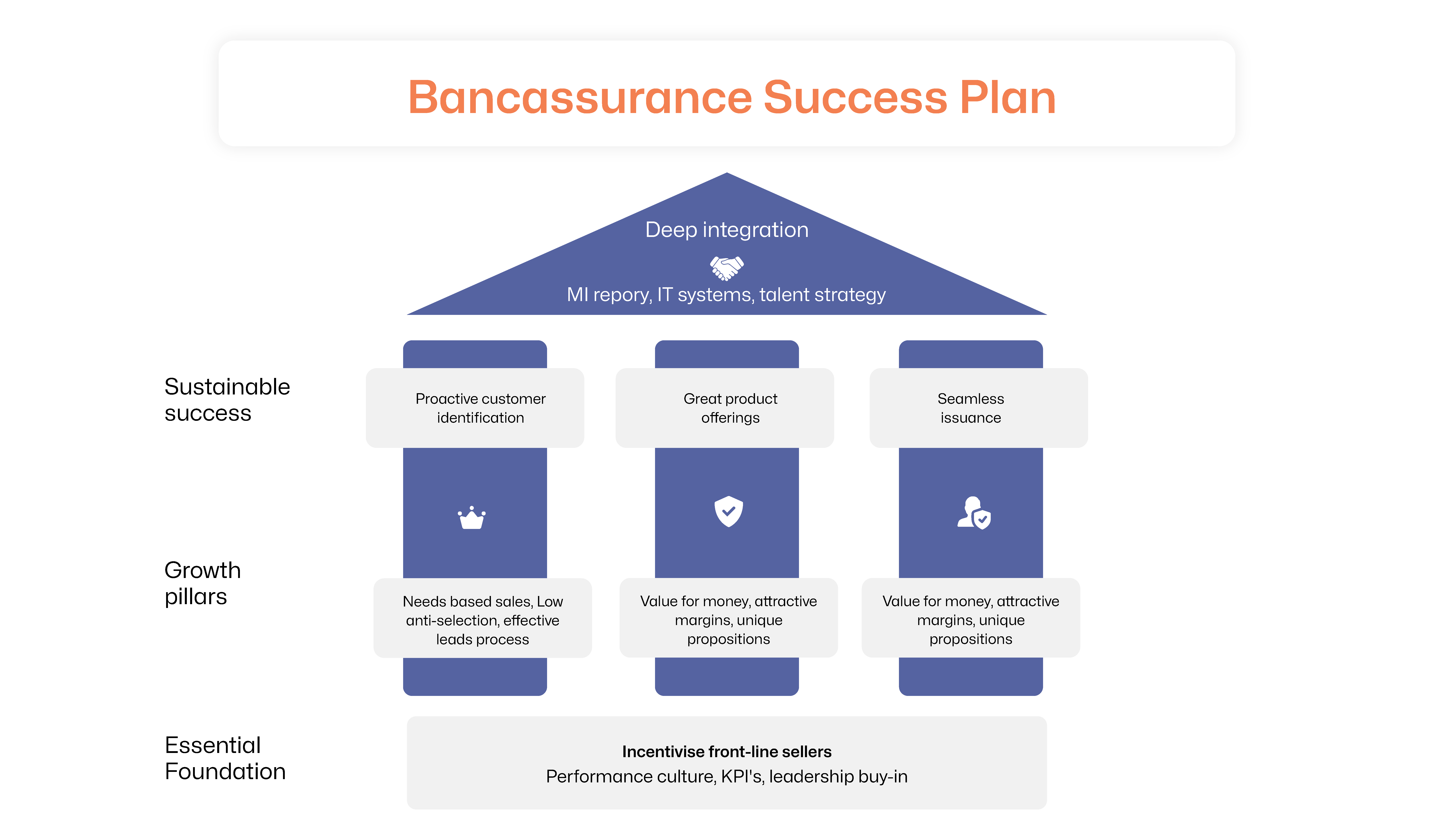
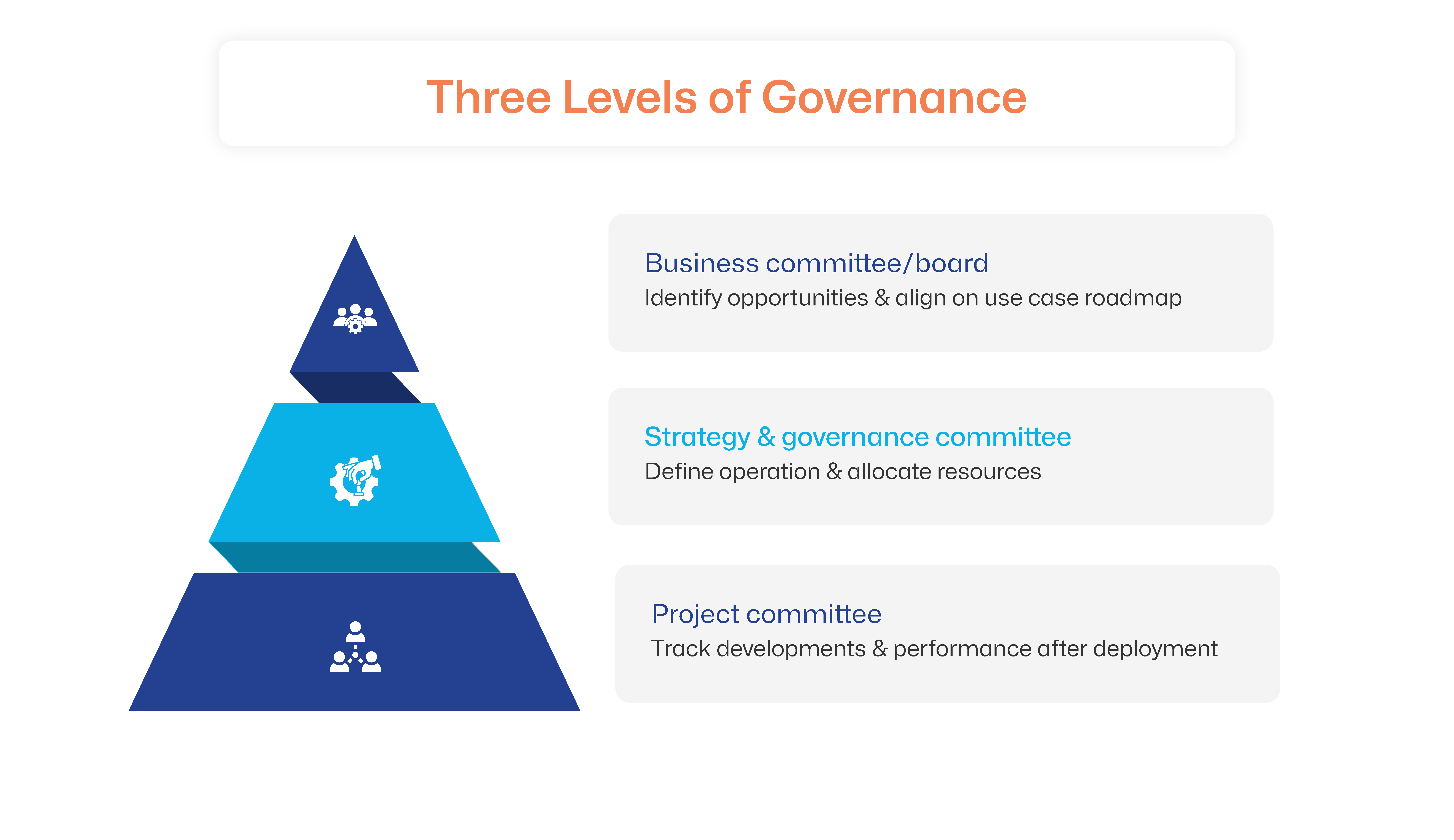
How to Build a Successful Bancassurance Partnership
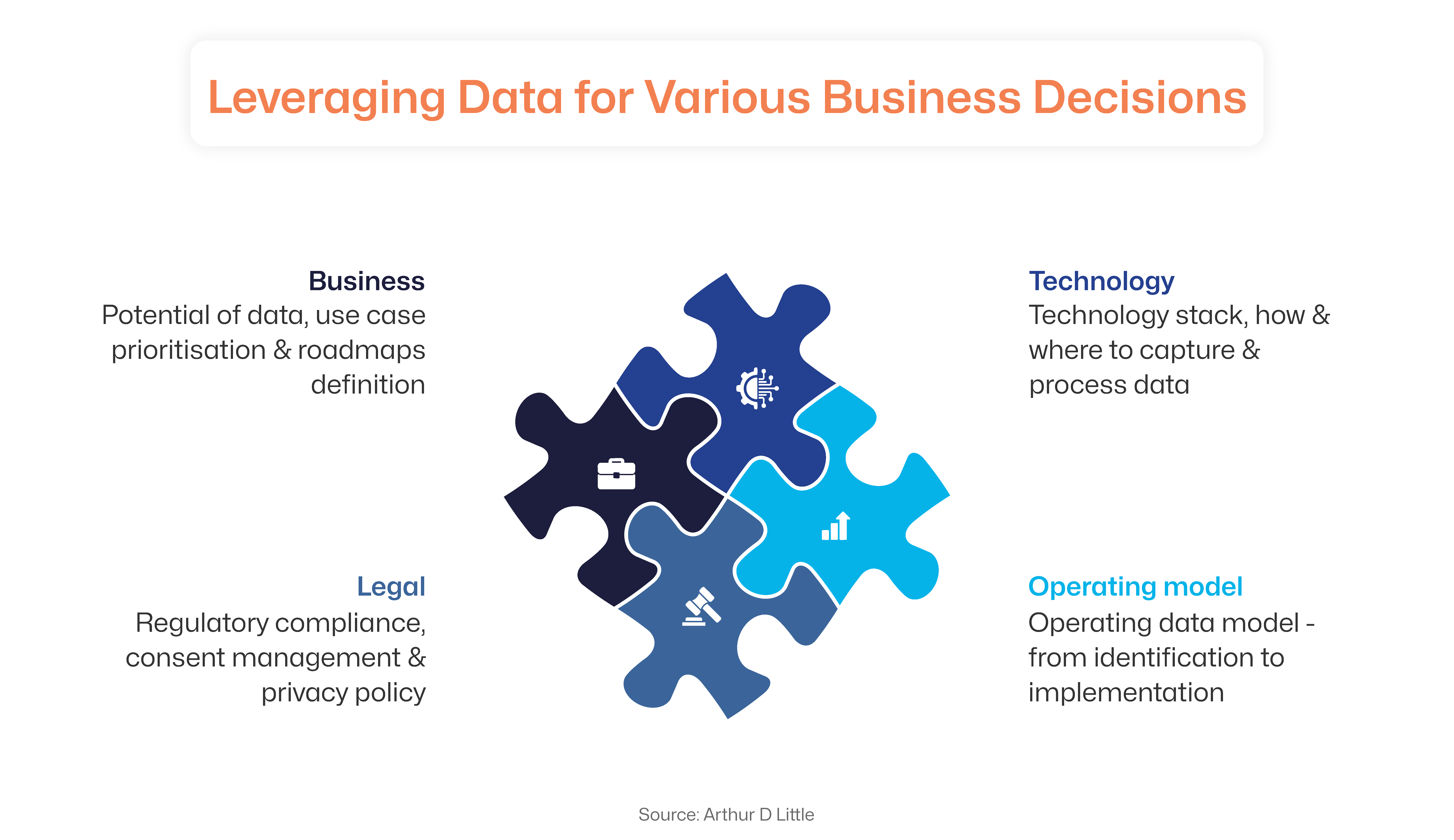
Bancassurance operations are complex to set up and maintain. Adopting industry best practices can be helpful. Carefully choosing a partner and adopting the right strategy is crucial to reaping the benefits of investments in technology, staff training and marketing. Technology is another key determinant for bancassurance success. It offers a competitive advantage in product development, distribution and risk assessment.
A. For Banks
A critical factor for bancassurance success is making banking culture more insurance-friendly. It requires the alignment of banking leaders and team members with the motives, regulations and processes of insurance.
Choose a Suitable Partner
The key is to develop a unified operating model and a common governance framework to deliver cohesive customer experiences.
Conduct Propensity Analysis
Leverage ML and predictive analytics to power intelligent cross-selling with the next best offer (NBO) and customer lifetime value (CLTV) analysis. This can also enable customer churn analysis and offer insights into opportunities to improve retention rates.
People Upskilling
Upskilling enables the adoption of agile work styles with technology assistance and adequate compensation for additional effort.
B. For Insurers
Since insurance products are being sold, insurers must do their share of work:
Customising Product Suites
This involves using banking data to refine insurance offerings and bundling insurance into credit and wealth products.
Platform Digitalisation
Here, insurtech, big data analytics and AI are employed for seamless policy issuance and claims management.
Knowledge Transfer
Ensuring adequate knowledge transfer and creating training plans could potentially accelerate the bancassurance rollout.
C. For Both
While separate efforts are crucial, working together on certain things makes collaboration more efficient and rewarding.
Compliance
Regulatory compliance with bancassurance guidelines is the shared responsibility of both partners. Third-party audits and automation technologies can facilitate collaborative compliance and security initiatives.
Process Reengineering
Both the bank and the insurance provider must work together to simplify customer journeys, eliminate friction in customer interactions, manage sales funnels and enable remote claims management.
Future of Bancassurance: Adopting a Unified Vision
The bancassurance landscape is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving customer expectations and intensifying regulatory oversight. Here’s a look at the key trends shaping its future.
The global bancassurance market is forecasted to reach $1.71 trillion by 2030.
Combining the Power of Analytics and AI
Leveraging telematics and AI to offer on-demand contextual coverage via mobile apps, online portals and third parties is key to deepening the penetration of insurance. Utilising virtual assistants for instant support and personalised interactions can be instrumental in retaining customers.
Developing API Ecosystems
Fuelling innovation through collaboration with diverse players in the financial landscape and third parties can unlock opportunities for coverage and inclusion.
Smart Contracts
Automating policy issuance, premium payments and claims processing with blockchain-based smart contracts can be a game-changer for bancassurance. Immutable records can enhance claims processing efficiency, enforcement of policy terms and maintaining regulatory guardrails while mitigating fraud
Mobile-First Strategies
The importance of delivering bancassurance products and services through mobile channels cannot be overstated. This is especially true for regions with high internet penetration, where mobility can accelerate bancassurance adoption. Mobile-first strategies can capitalise on the potential of emerging markets, especially in the APAC region, improving insurance access for the underserved and unserved populations.
Sustainability and ESG Integration
The future of bancassurance can be secured by embracing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices and offering aligned insurance and investment products. Socially responsible products that support vulnerable populations and combat climate change are likely to be adopted faster as climate awareness increases. Increasing transparency in ESG ratings and reporting can ensure accountability and drive sustainable growth.
IndiaFirst Life, a subsidiary of Bank of Baroda, is among the leaders in aligning ESG principles and insurance penetration goals. The company’s website features an ESG efforts section to highlight its sustainability efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is bancassurance, and how does it work?
Bancassurance is a convenient way for insurers to distribute and customers to buy insurance products via banking channels. This offers cost benefits to both the insurer and the customer, while banks enjoy partnership benefits, such as additional revenue streams, more customer data and extended customer longevity.
Is bancassurance different from traditional insurance sales?
The only difference between bancassurance and traditional insurance sales is the distribution channel. Traditionally, insurance distribution uses manual agents. On the other hand, in bancassurance, either banking personnel or digital channels are used.
What types of insurance products can be sold through bancassurance?
Bancassurance product types range from traditional life, health and automobile insurance to innovative pay-as-you-use, micro-insurance, and savings and investments-linked insurance.
What are the risks of bancassurance for banks and insurers?
Bancassurance does entail some potential risks. Customers may face limited product choices and lack the opportunity to compare insurance products from different providers. A conflict of interest could arise if bank employees prioritise insurance sales over providing unbiased financial advice. Also, insufficiently protected data sharing between banks and insurers may raise privacy issues. Both banks and insurers risk becoming overly dependent on each other’s income streams. Conversely, differing corporate cultures between the two entities could create operational challenges. The good news is that all these can be worked through with the help of regulatory oversight and advance planning.
How is digital technology changing bancassurance?
Digital technologies, such as insurtech and regtech, are revolutionising bancassurance by enhancing efficiency, personalising customer experiences and supporting new business models. AI and ML allow the 24/7 availability of banking and insurance support and enable data-driven risk assessment.
Is bancassurance available in all countries?
Bancassurance has penetrated several countries. However, regulations governing the distribution of insurance products through banks vary from country to country. Customers must check with their local banks to see if bancassurance is available in their region and learn about the regulatory guidelines. It is best to trust only licensed and compliant banks and insurers.
Which regulatory bodies regulate bancassurance in India?
In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDAI) together regulate bancassurance.
Who is involved in bancassurance?
Bancassurance is a partnership between a bank and an insurance company, governed by regulatory guidelines aimed at improving customer access to insurance.
Transform Your Bancassurance Strategy Today!
IMARC expects the Indian bancassurance market to reach a value of $172.4 billion by 2032. Capturing this opportunity requires a well-rounded approach. To maximise customer value and user experience in bancassurance, firms must align strategies, navigate data protection laws, and use insurtech and regtech to ensure bank-insurer coordination for data analytics. A structured approach unlocks data sharing potential, fostering innovation. Adapting with agility to evolving customer needs is crucial for sustained growth.
Zopper is a leading end-to-end insurtech provider, offering flexible, scalable and affordable insurance distribution solutions. Our pan-India footprint positions us to build a robust, unified ecosystem for seamless insurance operations. Contact us today to learn how our insurtech solutions can transform your business.







